

wordpress-seo domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /home/sehatnagar.com/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6114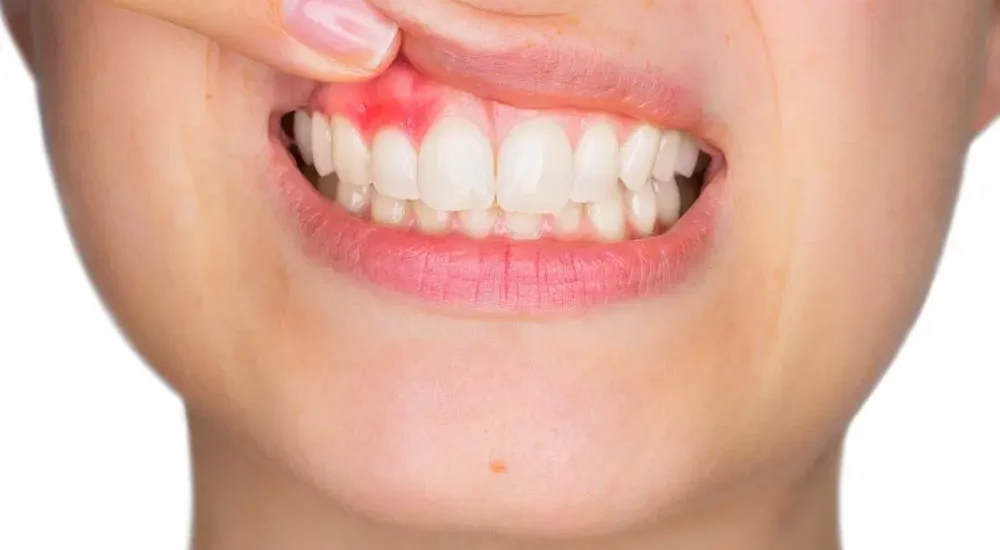
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gums, bone, and other supporting structures of the teeth. It is a prevalent oral health issue that can lead to serious consequences if left untreated. One of the most common concerns people have about periodontal disease is how long they can keep their teeth once diagnosed with the condition. In this extensive article, we will delve deeper into the various factors that influence the prognosis of teeth affected by periodontal disease and discuss comprehensive preventive measures and treatment options to preserve oral health.
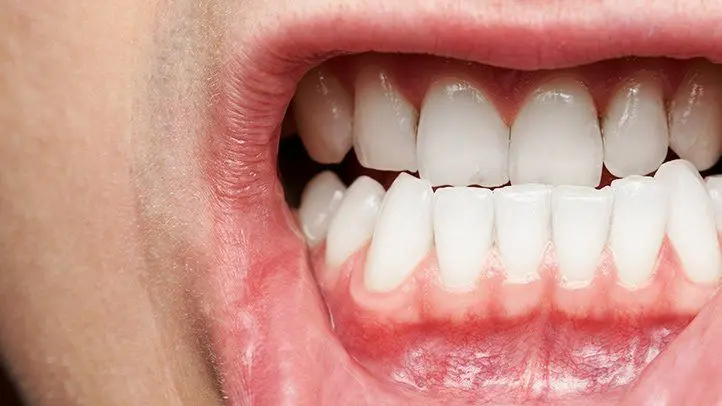
Periodontal disease begins as gingivitis, the inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of plaque and bacteria. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of the disease. Periodontitis leads to the destruction of the bone and tissues that support the teeth, ultimately leading to tooth mobility and loss.
The extent to which periodontal disease has progressed plays a significant role in determining tooth prognosis. Mild cases might be manageable with proper care, while advanced cases could result in irreversible damage.
Early detection and intervention are crucial for maintaining teeth affected by periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups allow for timely diagnosis and treatment, increasing the likelihood of preserving teeth.
People’s responses to periodontal disease can vary. Factors such as genetics, overall health, and immune system function can impact how the disease progresses and how well the body can fight it.
Diligent oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, can slow the progression of periodontal disease and help in retaining teeth.
Smoking and certain lifestyle choices can exacerbate periodontal disease, making it more challenging to maintain teeth. Quitting smoking and adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively influence the prognosis.
Conditions like diabetes and immune disorders can affect the body’s ability to fight periodontal disease. Proper management of these conditions is vital for oral health.
Periodontists, dentists specialized in treating gum diseases, offer various treatments such as scaling and root planing, periodontal surgery, and laser therapy. These treatments aim to remove infection and promote healing.
After initial treatment, regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor the disease’s progression and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
In some cases, antibiotics or antimicrobial mouth rinses might be prescribed to manage infection and inflammation.
Patients with periodontal disease should follow a meticulous oral care routine, including brushing with a soft-bristle toothbrush, using antimicrobial mouthwash, and flossing gently.
A diet rich in vitamins C and D, along with other nutrients, can support gum health. Consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
Chronic stress can worsen periodontal disease. Practicing stress-reduction techniques can positively impact oral health.
In cases of severe gum recession, gum grafting procedures can help cover exposed tooth roots, reducing sensitivity and improving aesthetics.
In some cases, despite the best efforts, tooth extraction may be unavoidable due to severe bone loss, extensive mobility, or infection. Your dentist or periodontist will make this decision after a thorough evaluation.
If tooth extraction becomes necessary, dental implants and prosthetics can offer a solution for replacing missing teeth. These options can restore function and aesthetics.
The longevity of teeth affected by periodontal disease depends on various factors, including disease severity, timely intervention, individual variability, oral hygiene practices, lifestyle choices, and systemic conditions. While periodontal disease can pose a significant threat to teeth, early detection, professional treatment, and consistent and comprehensive oral care can greatly improve the chances of preserving your natural teeth. Regular dental visits, open communication with your oral health care provider, and a holistic approach to oral and overall health are key to ensuring the best possible outcome for your oral health journey. Remember, every effort you put into maintaining your oral health contributes to a brighter, healthier smile that lasts a lifetime.
Teeth Bonding Before And After: Transforming Smiles With Cosmetic Dentistry