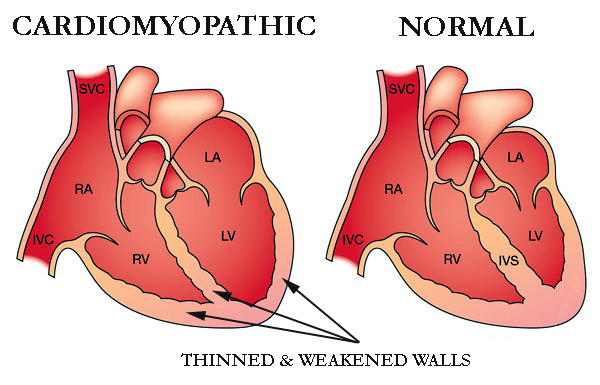
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that affects the structure and function of the heart. It is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged, thickened, or stiffened. This can result in a decrease in the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
Types of Cardiomyopathy
There are three main types of cardiomyopathy: dilated, hypertrophic, and restrictive cardiomyopathy. Additionally, there is also a rare type called arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Here is a brief overview of each type:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM): This is the most common type where the heart muscle becomes stretched and thin. It can lead to an enlarged heart. This can cause a decrease in the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. It cause leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and feet. DCM can be caused by genetic mutations, viral infections, or alcohol abuse, among other factors.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM): In this type the heart muscle becomes abnormally thick, making it harder for the heart to pump blood. HCM is often an inherited condition and can cause symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, and palpitations.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM): In RCM, the heart muscle becomes stiff and less elastic, which can lead to difficulty in filling the heart with blood. This can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and feet. RCM can be caused by genetic mutations, autoimmune diseases, or other conditions.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC): This is a rare type where the heart muscle in the right ventricle is replaced by fatty or fibrous tissue, which can cause abnormal heart rhythms. ARVC can be inherit, and symptoms can include palpitations, fainting, and sudden cardiac arrest.
It’s important to note that there are other, less common types of cardiomyopathy as well, and treatment options can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
The symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms:
- Shortness of breath: This is a common symptom and it can occur during physical activity or at rest.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak, even after resting, is another common symptom of cardiomyopathy.
- Swelling: Fluid buildup in the legs, ankles, and feet can occur in people.
- Chest pain or discomfort: This can be a symptom of dilated or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Palpitations: This is when you feel your heart beating irregularly or faster than normal.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: This can occur if your heart is not pumping blood effectively.
- Fainting: In severe cases fainting or passing out can occur.
It’s important to note that some people with cardiomyopathy may not experience any symptoms at all, and the condition may only be discovered during routine medical exams or tests.
Causes
The causes of cardiomyopathy can vary depending on the type of cardiomyopathy. However, some common causes include:
- Genetics: Some types cause due to genetic mutations, which can be inherit from one or both parents.
- Viral infections: Certain viral infections, such as myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), can lead to cardiomyopathy.
- Alcohol and drug abuse: Long-term alcohol abuse or drug abuse, such as cocaine or amphetamines, can damage the heart muscle and lead to cardiomyopathy.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, can cause inflammation and damage to the heart muscle.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure over time can cause the heart muscle to become thicker and stiffer, leading to cardiomyopathy.
- Coronary artery disease: This is a condition where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrow or blocked, which can lead to heart damage and cardiomyopathy.
- Other conditions: Certain other conditions, such as thyroid disorders, hemochromatosis (iron overload disorder), and sarcoidosis (inflammation of organs including the heart), can cause cardiomyopathy.
It’s important to note that in some cases, the cause of cardiomyopathy may be unknown. Understanding the cause of cardiomyopathy can help guide treatment and management of the condition.
Treatment
The treatment of cardiomyopathy depends on the type and severity of the condition, as well as the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol and caffeine, and exercising regularly, can help manage symptoms and improve heart function.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms and improve heart function.
- Implantable devices: In some cases, implantable devices such as pacemakers or defibrillators may be recommended to help regulate heart rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
- Surgery: Surgery may be recommended in some cases of cardiomyopathy, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, to remove excess heart tissue which cause block in blood flow.
- Heart transplant: In severe cases of cardiomyopathy, where other treatments have not been effective, a heart transplant may be recommended.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is right for you based on your individual needs and situation. Additionally, regular check-ups and monitoring are important to ensure that treatment is effective and to identify any potential complications.
Lifestyle
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and improve outcomes for people with cardiomyopathy. Here are some lifestyle changes that may be recommended:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease and can worsen symptoms of cardiomyopathy. Quitting smoking can improve heart function and overall health.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol and caffeine can worsen symptoms of cardiomyopathy. Your healthcare provider may recommend limiting or avoiding these substances altogether.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve heart function and overall health. However, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before starting an exercise program, as they can recommend a safe level of activity based on your individual needs.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet: Eating a diet that is low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium can help manage symptoms of cardiomyopathy and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Manage stress: Stress can be one of the worsen symptoms, so finding ways to manage stress is important. This may include techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Take medications as prescribed: If you are taking medications to manage symptoms of cardiomyopathy, it’s important to take them exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Making these lifestyle changes can help improve heart function and overall health, and may also reduce the risk of complications associated with cardiomyopathy. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a plan that is right for you based on your individual needs and situation.
Related