

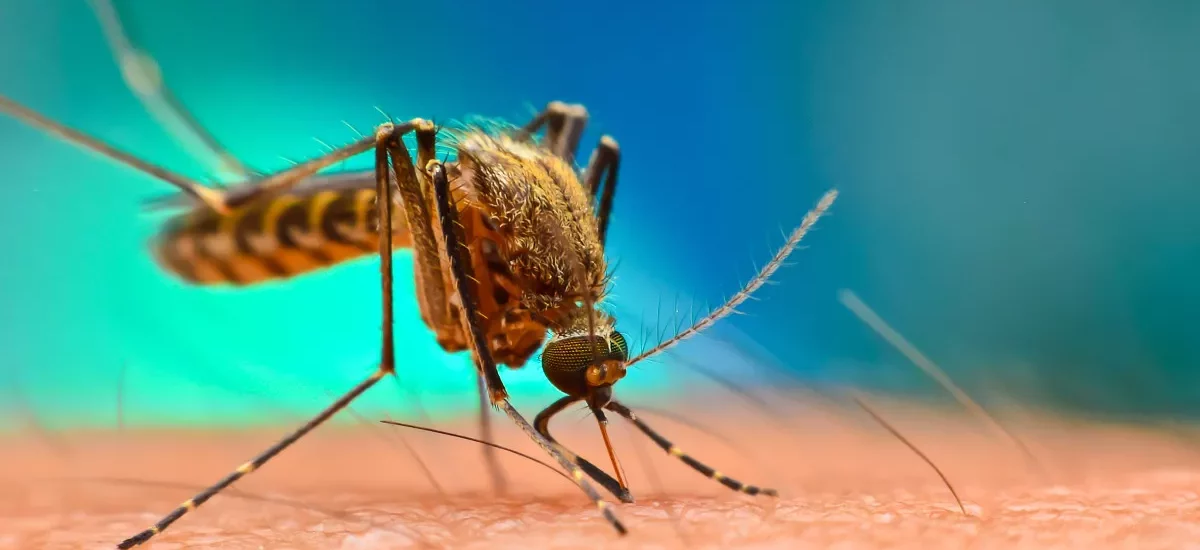
Malaria is a potentially life-threatening disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite. It is transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Once the parasites enter the body, they multiply in the liver and then infect red blood cells, leading to symptoms of Malaria such as fever, headache, muscle pain, and fatigue.
Malaria is a major public health concern, especially in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, where the Anopheles mosquitoes thrive. The disease can lead to serious complications, such as severe anemia, respiratory distress, and cerebral malaria, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
There are several types of malaria, each caused by a different species of the Plasmodium parasite. The most common types of malaria are:
The signs and symptoms of malaria can vary depending on the type of parasite causing the infection and the individual’s immune response. Some common signs and symptoms of malaria include:
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms and have recently traveled to an area where malaria is common, you should seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications and improve your chances of a full recovery.
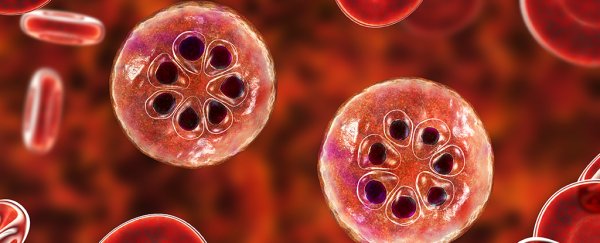
diagnosis and treatment are crucial for effectively managing malaria and preventing serious complications. If you suspect you may have malaria, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of malaria typically involves a blood test to confirm the presence of the parasite. This may be done using a rapid diagnostic test or by examining a blood smear under a microscope. Once malaria has been diagnosed, treatment usually involves the use of antimalarial medications, which can help to clear the parasite from the body and alleviate symptoms.
The specific treatment used will depend on the type of parasite causing the infection, as well as other factors such as the individual’s age and overall health. Commonly used medications for treating malaria include chloroquine, artemisinin-based combination therapies, and quinine. In some cases, hospitalization may be required for more intensive treatment and monitoring.
It is also important to take steps to prevent the spread of malaria. This includes using mosquito nets, wearing protective clothing, and using insect repellents to avoid mosquito bites. Travelers to areas where malaria is common should also take prophylactic medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
The symptoms and severity of malaria can vary depending on the type of parasite causing the infection, as well as the individual’s age, overall health, and immune status. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for managing malaria and preventing serious complications.
Prevention of malaria also involves taking steps to avoid mosquito bites and reducing exposure to areas where malaria is common. Here are some common measures for preventing malaria:
However, by taking these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting malaria and help prevent the spread of the disease.